How to Customize Git Log Output
The git log command is a powerful tool to see the history of a repository. It shows the commit messages, the author, the date, and the commit hash. But sometimes, you need to see more information, like the changes in a commit, the number of files changed, or the number of lines added or removed.
In this post, I will show you how to customize the output of the git log command to show more information about each commit.
Customizing the Output
To customize the output of the git log command, you can use the --pretty option. This option allows you to specify a format string that defines how each commit is displayed.
Here are some examples of format strings that you can use:
%h: Abbreviated commit hash%H: Full commit hash%an: Author name%ae: Author email%ad: Author date%s: Subject%d: Ref names%cr: Relative date
You can use these format strings to create a custom format for the git log output. For example, to show the commit hash, the author name, and the subject, you can use the following format string:
Format #1
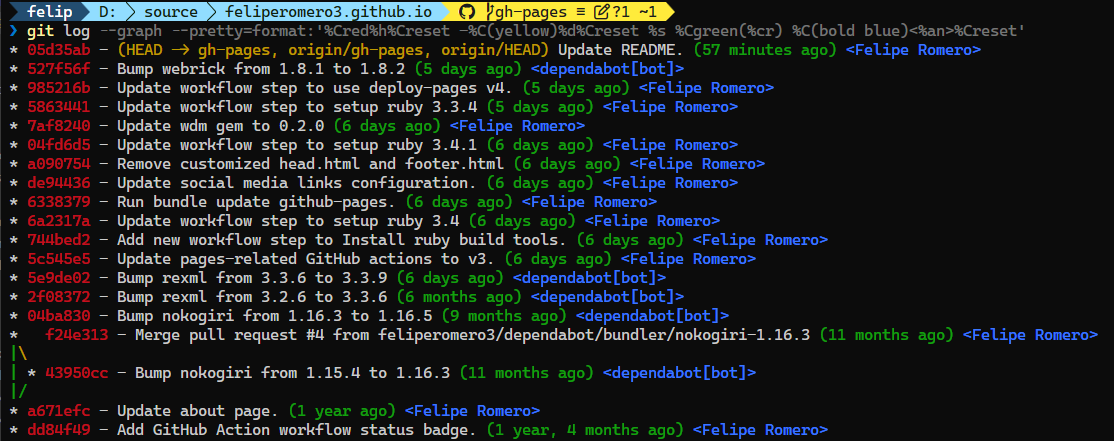
git log --graph --pretty=format:'%Cred%h%Creset -%C(yellow)%d%Creset %s %Cgreen(%cr) %C(bold blue)<%an>%Creset'This will show the abbreviated commit hash, subject, author (relative) date, and the author name of each commit.
Terminal output capture:
Format #2
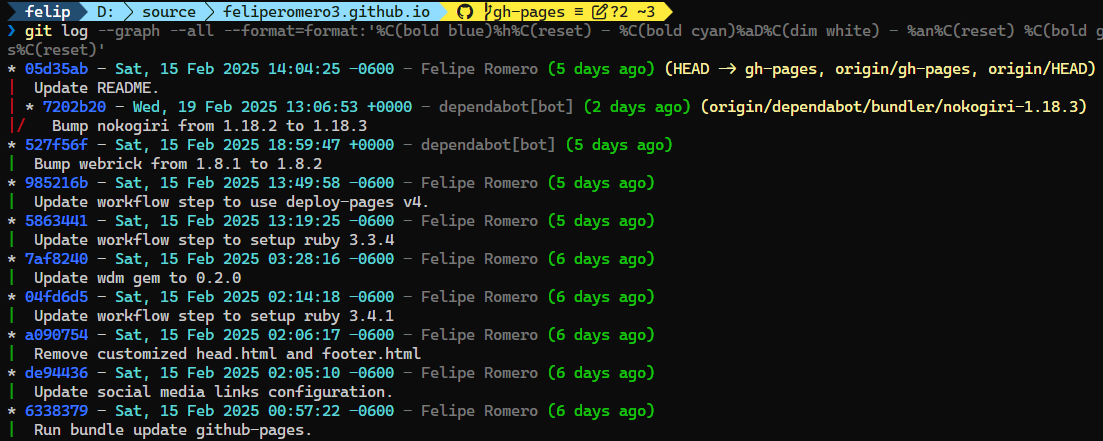
git log --graph --all --format=format:'%C(bold blue)%h%C(reset) - %C(bold cyan)%aD%C(dim white) - %an%C(reset) %C(bold green)(%ar)%C(reset)%C(bold yellow)%d%C(reset)%n %C(white)%s%C(reset)'This will show the abbreviated commit hash, the author name, the author date, and the subject of each commit.
Terminal output capture:
Format #3
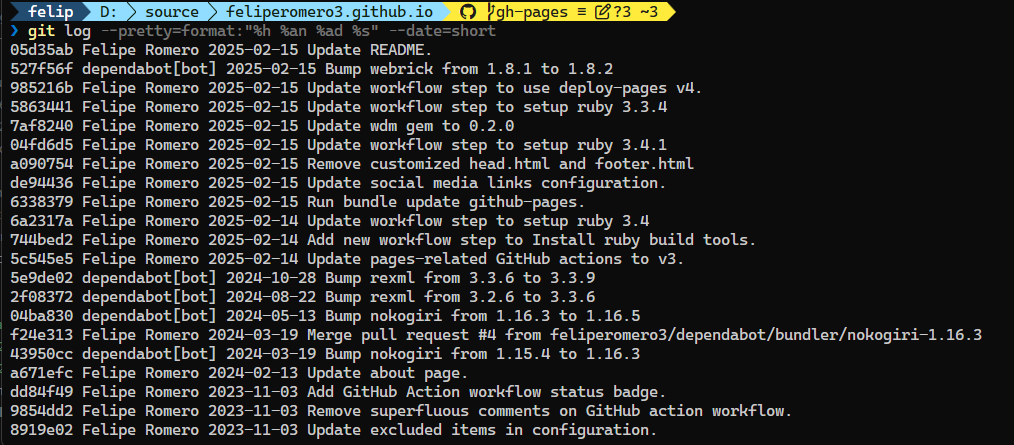
git log --pretty=format:"%h %an %ad %s" --date=shortIf you are not into colorful output, you can use a simple format string to show the abbreviated commit hash, the author name, the author date, and the subject of each commit.
Terminal output capture:
Bonus: Showing the changes in a commit
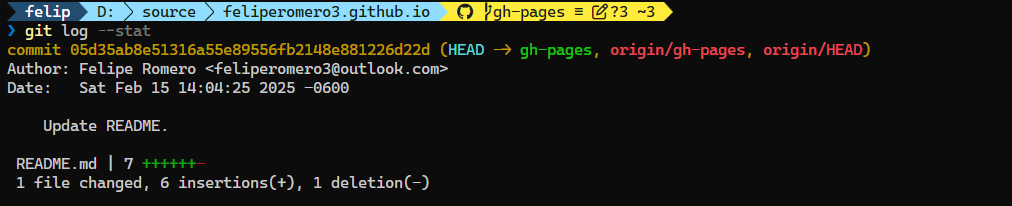
If you want to see the changes in a commit, you can use the --stat option. This option shows the number of files changed, the number of lines added, and the number of lines removed in each commit.
For example, to show the changes in each commit, you can use the following command:
git log --statThis will show the commit message, the author, the date, and the commit hash, as well as the changes in each commit.
Conclusion
The git log command is a powerful tool to see the history of a repository. By customizing the output of the git log command, you can see more information about each commit, such as the changes in a commit, the number of files changed, or the number of lines added or removed.